Transformers are not only of a single type. There are several options when choosing a transformer, such as power transformers, isolation transformers, toroidal transformers, EI transformers, SMPS transformers, etc. However, they all perform the basic function of transmitting power, signals or data from one point to another, each point being different from the other, with only a few aspects that make them unique.
A transformer uses a common oscillating magnetic circuit generated by its core to connect two or more circuits together. This becomes possible because it works in the form of mutual inductance according to the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a coil of wire magnetically induces a voltage into another coil located nearby.

ETD High Frequency Transformer
According to Faraday's Law of Magnetic Induction described above, a transformer is capable of increasing or decreasing the voltage to any desired level. The converted power can be distributed over great distances using a grid of towers and cables. The power to be distributed over such large distances is first converted to a higher level and then reduced to a lower, safer, available voltage when it reaches its destination, where it can be used to power electrical equipment in homes, commercial and industrial applications.
As mentioned above, there are several options for transformers, so it is important to choose the most appropriate transformer for your specific application. In this blog, we will discuss one of the most commonly used transformers today - the EI transformer.
Like any other transformer, the EI transformer consists of a primary winding that generates magnetic flux in the core when connected to a power source and a secondary winding that outputs a secondary current generated by the flux in the core. The transformer core provides a low reluctance path through which the magnetic flux can move from the primary to the secondary, thus creating a closed magnetic circuit.
As the name implies, in an EI transformer, the core is "E" and "I" shaped and is made from sheets of oriented electrical steel that are stamped and stacked to form an iron core. The primary and secondary windings are wound on bobbins, and multiple bobbins are placed on spindles and rotated to apply the windings. This unique approach makes it unique, helps automate, reduces manufacturing time, and provides insulation between the windings and the core. Ease of construction also makes EI transformers very economical to manufacture.
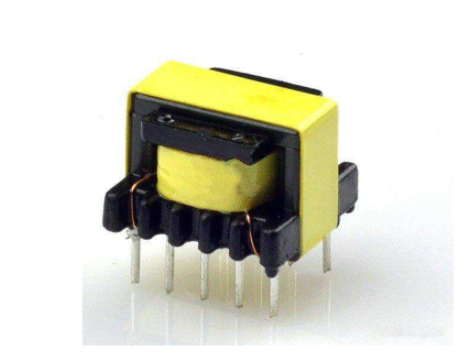
EI13 PCB electronic transformer
With its unique construction and the cost benefits associated with EI transformers, it certainly seems to be the best choice. However, this is not without its drawbacks. the main disadvantages of the EI transformer are that it comes with an unpleasant hum and its large size. However, if these disadvantages can be ignored, the EI transformer is the best choice for an easy-to-build, economical, easy-to-install transformer with a larger primary resistance and low coupling capacitance, thus preventing high-frequency common-mode noise mains AC. In summary, the EI transformer is an economical solution to many power conversion needs.

After considering all of the above factors, if you would like to purchase an EI transformer for your application, you can always contact SITONG, equipped with quality wiring, varnishing and connection terminators that provide excellent regulation and minimal temperature rise.